



PoE (Power over Ethernet) is a technology that allows data to be transmitted over Ethernet cables while simultaneously supplying power to connected devices. Traditionally, network devices (such as IP cameras, wireless access points, IP phones, etc.) required independent power supplies, which could lead to complex wiring, high costs, and dependence on power outlets. The advent of PoE technology has solved these problems, providing greater flexibility and convenience for the deployment of network devices.

History and Development of PoE
PoE technology was first proposed by Cisco Systems and standardized by the IEEE in 2003 as the IEEE 802.3af standard. With the continuous popularization and development of network equipment, PoE technology has gradually been widely applied and further developed. Later, the IEEE proposed an updated PoE standard, the IEEE 802.3at standard, also known as PoE+, which provides support for devices requiring higher power.
The Role and Advantages of PoE
• Simplified Cabling: Since PoE technology can transmit data and power through a single Ethernet cable, there is no need for additional power lines, simplifying the cabling process for network devices and reducing costs and complexity.
• Increased Flexibility: PoE technology allows network devices to be deployed more flexibly in various locations without being restricted by the location of power outlets, making it suitable for situations that require mobility or temporary deployment.
• Reduced energy consumption: Traditionally, many network devices must remain powered on even when not in use. PoE technology allows for flexible control of power supply to devices as needed, thereby reducing energy consumption.
• Enhanced reliability: The power supply provided by PoE technology is stable and reliable, reducing the risk of network outages caused by power failures.
The Role and Advantages of PoE
• Simplified Cabling: Since PoE technology can transmit data and power through a single Ethernet cable, there is no need for additional power lines, simplifying the cabling process for network devices and reducing costs and complexity.
• Increased Flexibility: PoE technology allows network devices to be deployed more flexibly in various locations without being restricted by the location of power outlets, making it suitable for situations that require mobility or temporary deployment.
• Reduced energy consumption: Traditionally, many network devices must remain powered on even when not in use. PoE technology allows for flexible control of power supply to devices as needed, thereby reducing energy consumption.
• Enhanced reliability: The power supply provided by PoE technology is stable and reliable, reducing the risk of network outages caused by power failures.
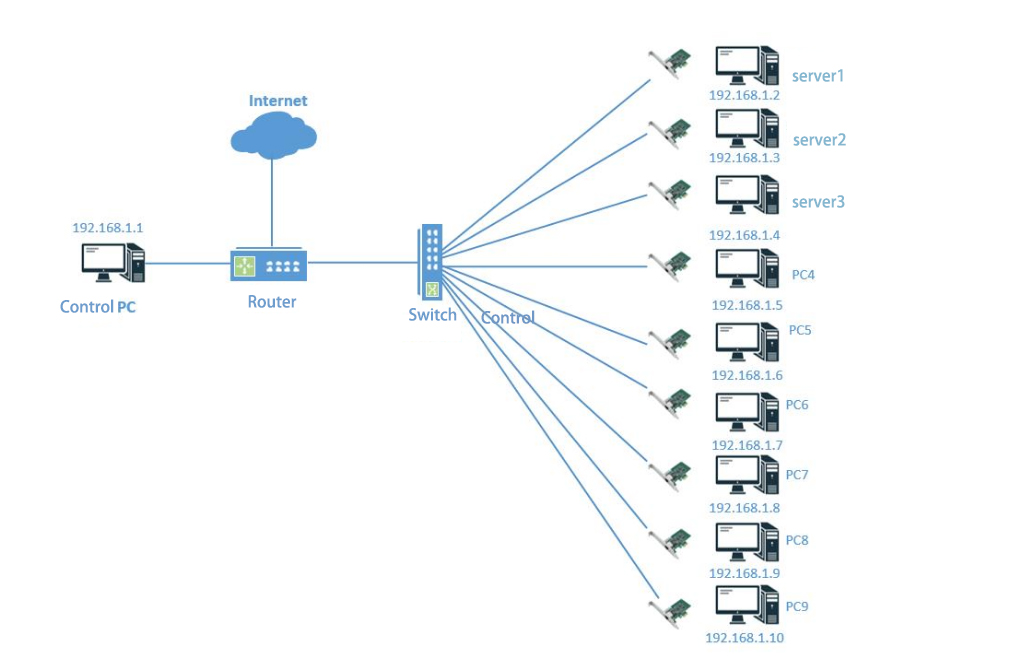
Components of PoE
•PoE Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE): Devices responsible for supplying power to equipment in a network, typically switches or dedicated PoE injectors.
•PoE Powered Devices (PD): Devices that receive power from PSE devices, such as IP cameras, IP phones, wireless access points, etc.
•PoE Middleware: Software or hardware components used to manage and monitor PoE networks, enabling tasks such as managing power supply devices and monitoring power consumption.
PoE standards
IEEE 802.3af Standard
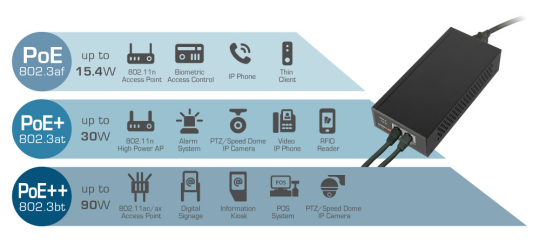
IEEE 802.3af is a networking standard commonly referred to as PoE (Power over Ethernet), which enables power to be supplied to network devices via Ethernet cables. This standard was officially released in 2003, marking the beginning of a new era in network design.
The 802.3af standard provides the foundation for directly powering various devices through network cables, including IP cameras, VoIP phones, and WLAN access points. It can provide up to 15.4 watts of power output per port, but due to power loss in the cable, the actual available power is approximately 12.95 watts.
The introduction of this standard has made the deployment of network devices more flexible and convenient, eliminating the need for separate power lines and reducing costs and complexity. Additionally, PoE technology offers higher reliability and energy efficiency by transmitting both power and data over Ethernet cables, thereby reducing reliance on power outlets and lowering energy consumption.
IEEE 802.3at Standard
IEEE 802.3at is a networking standard also known as PoE+ (Power over Ethernet Plus), which is an improvement and extension of the IEEE 802.3af standard (PoE). The 802.3at standard was officially released in 2009, aiming to provide a PoE solution with higher power output to meet the needs of high-performance network devices requiring more power.
The 802.3at standard expands the power output capabilities of PoE, enabling each port to deliver up to 30 watts of power output. In comparison, the 802.3af standard can only provide up to 15.4 watts of power output. This allows the 802.3at standard to support a wider range of devices, including those requiring higher power, such as dual-band wireless access points, PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras, and VoIP video phones.
In addition to providing higher power output, the 802.3at standard introduces new features such as power management and classification to enhance the efficiency and reliability of power transmission. These features enable PoE+ devices to manage power supply more intelligently, dynamically adjust power output, improve energy efficiency, and pave the way for future network infrastructure development.
IEEE 802.3af vs 802.3at
IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at are two different PoE (Power over Ethernet) standards, with the main differences being their power output capabilities and the types of devices they support.
Power Output Capabilities:
802.3af Standard:
Provides a maximum power output of 15.4 watts.
• The actual available power is approximately 12.95 watts due to power loss during transmission.
• 802.3at standard (also known as PoE+):
• Provides a maximum power output of 30 watts, which is twice that of the 802.3af standard.
• At least 25.5 watts of power is provided at the device end, which is more than the 802.3af standard.
Supported Device Types:
• 802.3af standard:
• Suitable for low-power devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, wireless access points, etc.
Not suitable for certain device types that require more power due to power limitations.
802.3at standard:
Customized for devices requiring higher power.
Supports a wider range of devices, including dual-band wireless access points, PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras, VoIP video phones, etc., which require more power to operate efficiently.
IEEE 802.3af vs 802.3at
IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at are two different PoE (Power over Ethernet) standards, with the main differences being their power output capabilities and the types of devices they support.
Power Output Capabilities:
802.3af Standard:
Provides a maximum power output of 15.4 watts.
• The actual available power is approximately 12.95 watts due to power loss during transmission.
• 802.3at standard (also known as PoE+):
• Provides a maximum power output of 30 watts, which is twice that of the 802.3af standard.
• At least 25.5 watts of power is provided at the device end, which is more than the 802.3af standard.
Supported Device Types:
• 802.3af standard:
• Suitable for low-power devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, wireless access points, etc.
Not suitable for certain device types that require more power due to power limitations.
802.3at standard:
Customized for devices requiring higher power.
Supports a wider range of devices, including dual-band wireless access points, PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras, VoIP video phones, etc., which require more power to operate efficiently.
